Thermodynamics of Equilibrium
Thermodynamics of Equilibrium: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Relationship between Equilibrium Constant (K) & Reaction Quotient (Q) and Gibbs Free Energy Change (ΔG) etc.
Important Questions on Thermodynamics of Equilibrium
The Haber’s process for the formation of at is . Which of the following is the correct statement?
The enthalpy and entropy change for the reaction
are respectively. The temperature at which the reaction will be in equilibrium is
A schematic plot of ln versus inverse of temperature for a reaction is shown below
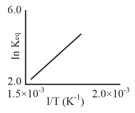
The reaction must be –
In a one-litre flask, moles of undergoes the reaction . The progress of product formation at two temperatures (in Kelvin), and , is shown in the figure:
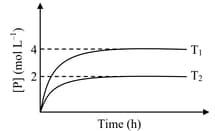
If and , then the value of is
[ and are standard Gibb's free energy change for the reaction at temperatures and , respectively.]
What is the (approx) partial pressure of at equilibrium at ?
Select the correct option about for the following reaction
(Given: , molar volume of water at )
for the reaction
the thermodynamic equilibrium constant at is:
Which of the following is correct at equilibrium?
Select the graph which can be used to determine standard free energy of the reaction given below:
Assume that the reaction is at equilibrium.
Among the following set of conditions, which condition necessarily holds true for a non-feasible process?
(Where, equilibrium constant)
Calculate the temperature given that the value of and of are and the reactants and is in equilibrium with .
Calculate for the following change, if vapour pressure of water is at .
Which is correct for the combustion reaction occurring in an automobile is .
The value of for the following reaction at is:
Given, standard Gibbs energy change at the given temperature is
For the following reaction,
the . What is the value of of the reaction at ?
For a spontaneous chemical reaction, the value of must be negative and the value of must be greater than __
Given:
Consider that for a hypothetical reaction, and are and at What is the equilibrium constant for the reaction at
For a hypothetical reaction, and At what temperature (in Celsius), the reaction is at equilibrium?
For the given reaction, concentrations are given as: is and in the presence of excess water. What is the value of at at some non-equilibrium condition?
Consider the curve between and . Which plot will be correct for exothermic reaction?
